Overview of the API
Before we go any further, let's take a quick tour of the API provided by Socket.IO:
Common API
The following methods are available for both the client and the server.
Basic emit
As we have seen in step #4, you can send any data to the other side with socket.emit():
- From client to server
- From server to client
Client
socket.emit('hello', 'world');
Server
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
socket.on('hello', (arg) => {
console.log(arg); // 'world'
});
});
Server
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
socket.emit('hello', 'world');
});
Client
socket.on('hello', (arg) => {
console.log(arg); // 'world'
});
You can send any number of arguments, and all serializable data structures are supported, including binary objects like ArrayBuffer, TypedArray or Buffer (Node.js only):
- From client to server
- From server to client
Client
socket.emit('hello', 1, '2', { 3: '4', 5: Uint8Array.from([6]) });
Server
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
socket.on('hello', (arg1, arg2, arg3) => {
console.log(arg1); // 1
console.log(arg2); // '2'
console.log(arg3); // { 3: '4', 5: <Buffer 06> }
});
});
Server
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
socket.emit('hello', 1, '2', { 3: '4', 5: Buffer.from([6]) });
});
Client
socket.on('hello', (arg1, arg2, arg3) => {
console.log(arg1); // 1
console.log(arg2); // '2'
console.log(arg3); // { 3: '4', 5: ArrayBuffer (1) [ 6 ] }
});
Calling JSON.stringify() on objects is not needed:
// BAD
socket.emit('hello', JSON.stringify({ name: 'John' }));
// GOOD
socket.emit('hello', { name: 'John' });
Acknowledgements
Events are great, but in some cases you may want a more classic request-response API. In Socket.IO, this feature is named "acknowledgements".
It comes in two flavors:
With a callback function
You can add a callback as the last argument of the emit(), and this callback will be called once the other side has acknowledged the event:
- From client to server
- From server to client
Client
socket.timeout(5000).emit('request', { foo: 'bar' }, 'baz', (err, response) => {
if (err) {
// the server did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(response.status); // 'ok'
}
});
Server
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
socket.on('request', (arg1, arg2, callback) => {
console.log(arg1); // { foo: 'bar' }
console.log(arg2); // 'baz'
callback({
status: 'ok'
});
});
});
Server
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
socket.timeout(5000).emit('request', { foo: 'bar' }, 'baz', (err, response) => {
if (err) {
// the client did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(response.status); // 'ok'
}
});
});
Client
socket.on('request', (arg1, arg2, callback) => {
console.log(arg1); // { foo: 'bar' }
console.log(arg2); // 'baz'
callback({
status: 'ok'
});
});
With a Promise
The emitWithAck() method provides the same functionality, but returns a Promise which will resolve once the other side acknowledges the event:
- From client to server
- From server to client
Client
try {
const response = await socket.timeout(5000).emitWithAck('request', { foo: 'bar' }, 'baz');
console.log(response.status); // 'ok'
} catch (e) {
// the server did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
}
Server
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
socket.on('request', (arg1, arg2, callback) => {
console.log(arg1); // { foo: 'bar' }
console.log(arg2); // 'baz'
callback({
status: 'ok'
});
});
});
Server
io.on('connection', async (socket) => {
try {
const response = await socket.timeout(5000).emitWithAck('request', { foo: 'bar' }, 'baz');
console.log(response.status); // 'ok'
} catch (e) {
// the client did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
}
});
Client
socket.on('request', (arg1, arg2, callback) => {
console.log(arg1); // { foo: 'bar' }
console.log(arg2); // 'baz'
callback({
status: 'ok'
});
});
Environments that do not support Promises (such as Internet Explorer) will need to add a polyfill or use a compiler like babel in order to use this feature (but this is out of the scope of this tutorial).
Catch-all listeners
A catch-all listeners is a listener that will be called for any incoming event. This is useful for debugging your application:
Sender
socket.emit('hello', 1, '2', { 3: '4', 5: Uint8Array.from([6]) });
Receiver
socket.onAny((eventName, ...args) => {
console.log(eventName); // 'hello'
console.log(args); // [ 1, '2', { 3: '4', 5: ArrayBuffer (1) [ 6 ] } ]
});
Similarly, for outgoing packets:
socket.onAnyOutgoing((eventName, ...args) => {
console.log(eventName); // 'hello'
console.log(args); // [ 1, '2', { 3: '4', 5: ArrayBuffer (1) [ 6 ] } ]
});
Server API
Broadcasting
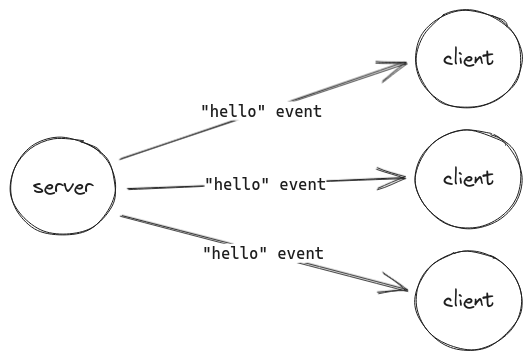
As we have seen in step #5, you can broadcast an event to all connected clients with io.emit():
io.emit('hello', 'world');
Rooms
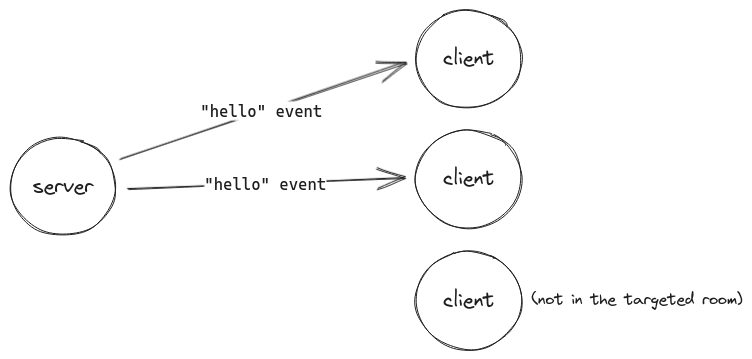
In Socket.IO jargon, a room is an arbitrary channel that sockets can join and leave. It can be used to broadcast events to a subset of connected clients:
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
// join the room named 'some room'
socket.join('some room');
// broadcast to all connected clients in the room
io.to('some room').emit('hello', 'world');
// broadcast to all connected clients except those in the room
io.except('some room').emit('hello', 'world');
// leave the room
socket.leave('some room');
});
That's basically it! For future reference, the whole API can be found here (server) and here (client).